Cyber Underwriting: Identifying a Business's True Digital Risk

Over the last year, it's no longer business as usual, and the business world and each of us are adapting fast to evolving global scenarios. One of the biggest changes has been the high pace of digitization across industries and consumer groups. With this shift, however, comes a greater risk of cyber threats. It’s not surprising then that there has been a huge spike in ransomware attacks, leading to a loss of critical information for businesses and they are turning to insurance to cover them. Insurance companies are still navigating the waters when it comes to cyber underwriting for the new breed of threats.
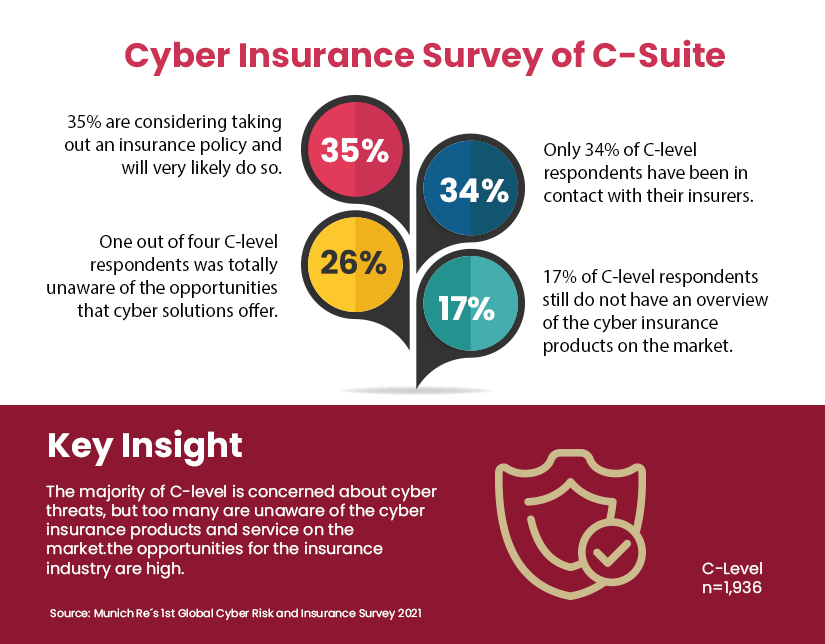
Cyber underwriting is a whole different ball game for insurers as it is intangible, borderless and fast-changing. Yet, investing in cyber underwriting can be well worth it for insurance providers as it is estimated to be a $70 billion service within the next 10 years. Currently, only an estimated 28% of small business owners have opted for commercial insurance policies. This means there’s a sizable portion of the market to be tapped into. How are cyber insurers preparing themselves to make the most of this opportunity?
Cyber underwriting, the work is never done
Cyber underwriting is by no means a ‘new’ service (it has been around for about 10 years) but as cyber threats have been getting more sophisticated, cyber insurers need to keep one step ahead. Definity a difficult ask when the enemy is like the Green Goblin supervillain (Norman Osborne) who can hack into the most advanced technology on the planet and make it his own secret weapon.,
That's why the one key difference in the modern cyber insurance underwriting process is the extent of information requested at the time of underwriting. Originally, only surface-level actuary information such as the revenue of a company, number of data records, and existing cybersecurity measures in place were requested. Today’s cyber risk underwriters, MGAs, and agents need a lot more data to be able to make an accurate estimation of risk. They often go deep into the company’s technological infrastructure, including the complete list of domains, details of the email servers, and the type of cybersecurity software used.
Additionally, the nature of commercial insurance policies offered is also changing from ‘recovery’ to ‘protection’. Rather than simply offering resources to businesses to mitigate losses from a cyberattack, cyber insurers are promoting preventative measures that can help avoid these attacks in the first place. This change in approach can make cyber insurance more profitable for insurers. This also means that underwriters need to be even more aware of the different types of cyber threats posed and the efficacy of various cybersecurity measures. This is the only way for a cyber underwriter to accurately understand cyber risks and price them. Cyber threat underwriters need to be grounded in technology.
Having a stronger cyber insurance underwriting process
Given the huge demand cyber insurance is predicted to generate, insurers need to create a strong cyber underwriting process to be able to successfully meet this demand. Here are three key steps to boosting your firm’s insurance underwriting process.
-
Assemble a complete cyber insurance team
Cyber underwriting deserves a dedicated team of specialists, much like other functions of underwriting. Many insurance firms that already offer commercial insurance policies might have only a small team, maybe even just one cyber underwriter to handle it. In cases where firms are offering this service for the first time, it can be tempting to use the same underwriters from other functions for cyber insurance as well. However, given the volume of actuary information and depth of cyber knowledge required, you will need a dedicated team of specialized underwriters for cyber insurance. Your cyber insurance team should also include specialists from legal, compliance, and information security to gain a truly accurate view of cyber insurance policies and claims.
-
Identify sources of cyber risks
Cyber risk underwriters are going to need a wealth of information to make accurate estimations of cyber risks. You will need to identify early on the parameters against which underwriters should evaluate policy applicants. Some of these can include:
-
Robustness of existing ransomware protection software and firewalls: There should also be strong executive leadership buy-in for cybersecurity strategies.
-
Frequency and competency of cybersecurity audits: Past cyber threats and resulting losses should also have been closely monitored. This indicates how vigilant a business is about preventing cyberattacks.
-
Compliance with privacy and data security regulations: Companies should adhere to global and regional security regulations and should ideally have a team that reviews compliance to these norms regularly.
-
Cybersecurity measures to accommodate for remote work: Employees should be given adequate training to identify phishing attempts (eg. through social engineering). If this is not conducted and there is no clear escalation protocol for employees to flag hacking attempts, this can suggest higher cyber risk.
-
Business continuity and recovery action plan: In the event of a cyberattack, recovery strategy should be clearly assigned to members within the organization. Lack of a clear strategy or reserves in the event of an attack is a negative signal.
-
Security controls when working with external vendors: The extent of data shared with these vendors, cybersecurity measures for data-in-transit, etc. are indicators of strong measures taken.
These parameters will need to be adjusted and adapted to different businesses based on the type of work they perform. It can be useful to have templates for various types of businesses to make it easier for cybersecurity underwriters to assess cyber risks.
-
Leverage advanced analytics
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are powerful tools to help underwriters process data and understand patterns quickly. Analytics can create industry-specific cybersecurity benchmarks and evaluate a specific company’s performance against them to identify how at-risk they are. AI can also scan a company’s complete history of cyberattacks and associated loss to identify recurring patterns. This data isn’t just useful for underwriters, but also for insured companies to prevent future attacks.
There are also a number of tools that can run a scan of a company’s domains, email servers, and databases to identify vulnerabilities. Sensor analytics can immediately detect anomalies and report them. These results can help underwriters understand the possibilities of a cyberattack and estimate a suitable price.
Cyber insurance can be a challenging prospect for underwriters because of the lack of tangible assets to estimate. With cyber attacks becoming ever more sophisticated, underwriters need to constantly stay on top of the latest trends to identify vulnerabilities. It is impossible to do that without intelligent automation tools helping cyber risk underwriters to create personalized commercial insurance policies for businesses. With the world becoming increasingly digital, cyber insurance will undoubtedly help insurance firms modernize and expand their services.
Topics: A.I. in Insurance



.jpg)