The Future of Work in Insurance: Evolution of Embedded Marketplaces and Insurance Ecosystems

Experts predict that by 2025 there will be one trillion connected devices. This includes existing categories such as smartphones, cars, and smartwatches that will be joined by new categories that could include medical devices, clothing, eyewear, and others that might still surprise us. The resulting deluge of data will have an effect on the way we do business and insurance is facing changes in the workplace that needs to be prepared for.
Don’t miss our earlier article that discusses the evolving roles and skills that will change the insurance workplace of the future.
This article provides insights into ways Insurance will expand into new industry sectors and will thrive on ecosystem collaboration. Current trends indicate that the future of work in insurance will require employees to adapt to an environment that will be dictated by connectivity and access to a stream of real-time data.
Continuous Learning and Adaptability
The insurance industry will place a greater emphasis on continuous learning and adaptability in the future of work. Insurance professionals will need to keep pace with rapidly evolving technologies, industry regulations, and customer expectations. Lifelong learning, upskilling, and reskilling initiatives will be integral to career growth and maintaining relevance in a dynamic industry. Insurance companies will invest in training programs, digital learning platforms, and partnerships with educational institutions to ensure their workforce remains competent and adaptable.
As technology rapidly evolves, insurance professionals will need to continuously update their skills and knowledge to leverage new tools and platforms effectively. For example, underwriters may need to learn how to utilize advanced data analytics and AI-driven underwriting models to make more accurate risk assessments and tailor policies to individual customers.
-
Increasing dependence on data analytics: With the increasing availability of data, insurance companies will rely on data analytics to gain valuable insights into customer behaviors, market trends, and risk assessment. Employees will need to develop data literacy skills to interpret and apply these insights effectively. For instance, claims adjusters may use data analytics to detect fraudulent claims patterns and streamline the claims process.
-
Regulatory Changes: The insurance industry operates in a highly regulated environment, with rules and regulations that can change frequently. Compliance officers will need to undergo regular training to ensure adherence to new regulations and avoid penalties. Technology is expected to play a role in helping insurance professionals keep pace with changing regulations
Embedded insurance will cross new frontiers
Embedded insurance is a concept that involves integrating insurance products and services seamlessly into the customer journey of non-insurance businesses. It allows customers to access insurance coverage as part of their interactions with other industries or platforms.
Embedded insurance is still in unchartered territory and has massive growth potential. This analogy will put the future of embedded insurance into a better perspective. Today, embedded insurance is like a junior league soccer game. The game plan is for everyone to run around chasing the ball. The future of embedded insurance is more like a professional league soccer game, where players are spread out and there is more passing. This way the team can quickly evade obstacles and carry the ball further up the field. That’s the beauty of embedded insurance’s future, seamlessly reaching customers anywhere and everywhere. Insurance marketing and technology will evolve to meet these new advancements. And insurance core platforms must be future-ready for this change.
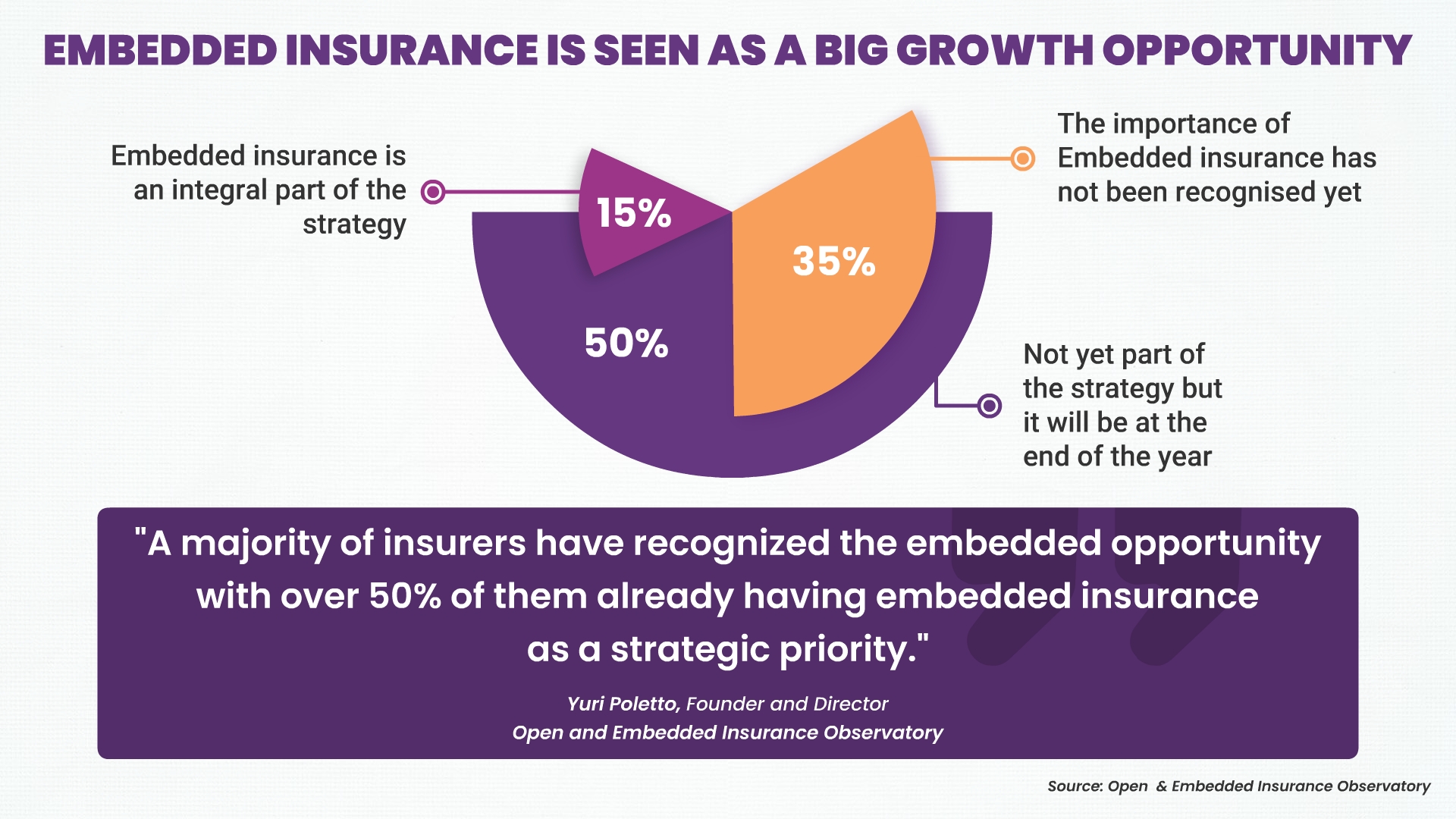
Embedded insurance will expand into new industries
Insurance will be largely distributed by non-insurance brands. While embedded insurance is already prevalent in industries like travel, e-commerce, and ride-sharing, the future will see its expansion into new sectors. We can expect to see insurance integrated into areas such as healthcare, real estate, mobility services, and subscription-based platforms. This expansion will enable customers to access insurance coverage in a wider range of contexts and simplify their insurance needs. insurtech companies in America are actively working on building technology platforms to facilitate the integration of insurance into various industries.
In a report by McKinsey & Company, it was estimated that embedded insurance could reach a market share of $3 trillion by 2030 globally.
From Microinsurance to Embedded Marketplaces
Today, the focus is more on embedding microinsurance products that provide a simple solution at the point of need eg. travel insurance or product insurance. The future of embedded insurance is expected to evolve from microinsurance offerings to more complex and comprehensive embedded insurance marketplaces. Let's explore this progression in detail:
Microinsurance addresses only specific risks: Microinsurance involves providing small, affordable insurance policies to individuals with low incomes or specific needs. In the past, embedded insurance primarily focused on microinsurance solutions, addressing narrow risks such as coverage for a single item or short-duration protection. For example, microinsurance might include coverage for a single trip or a specific event.
An embedded marketplace for insurance is a platform or ecosystem where multiple insurance products from different insurers are seamlessly integrated into non-insurance products or services. It serves as a one-stop shop for customers to access various insurance offerings while using a non-insurance platform or service. This integration creates a holistic customer experience, providing convenient access to insurance coverage tailored to the specific comprehensive insurance options, catering to various customer segments and needs.
-
Diversity of Insurers: Embedded marketplaces collaborate with multiple insurance providers, offering customers a choice between different insurers and coverage options. This diversity allows users to compare and select insurance products that best suit their requirements. In contrast, microinsurance offerings are often provided by a single insurer or a limited number of insurers.
-
Customer Experience: An embedded marketplace enhances the customer experience by providing a seamless insurance buying process within the non-insurance platform. Users can easily browse and purchase insurance coverage without leaving the platform they are using. On the other hand, the microinsurance format, while convenient, may have more limited coverage options and might require separate transactions from the primary purchase.
-
Target Audience: Embedded marketplaces appeal to a broader range of customers, including those seeking comprehensive insurance coverage beyond microinsurance limits. They cater to various industries and use cases, such as travel, retail, health, and more.
-
Complexity of Coverage: An embedded marketplace may offer more complex insurance products, including broader coverage and higher policy limits. Microinsurance, on the other hand, tends to offer simple, predefined coverage for specific events or risks.
-
Technology and Data Integration: Embedded marketplaces leverage advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, to offer real-time risk assessment, personalized recommendations, and dynamic pricing. Microinsurance may not involve such sophisticated data-driven features.
Insurance ecosystems will change business as we know it
In 2030 and beyond, insurance collaboration and ecosystems are expected to undergo significant changes driven by technological advancements, changing customer expectations, and industry disruptions.
Here are some key ways in which insurance collaboration and ecosystems may evolve:
Ecosystem Orchestration: Insurers may take on a more proactive role in orchestrating ecosystems. They will act as ecosystem managers, facilitating seamless interactions between partners, data exchange, and ensuring a unified customer experience across various touchpoints.
Data Collaboration and Sharing: Ecosystem partnerships will involve sharing and analyzing vast amounts of data among various partners. Insurers will collaborate with tech companies and data providers to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, risk assessment, and market trends.
Insurtech Integration: The rise of insurtech companies will lead to more collaboration between traditional insurers and startups. There will be increased reliance on AI bots to augment human capabilities
Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Blockchain technology will enable secure and transparent collaboration between insurers, reinsurers, brokers, and other ecosystem partners. Smart contracts will automate processes and claims settlement, improving efficiency and reducing fraud.
Ecosystems for Emerging Risks: Insurance ecosystems will be designed to address emerging risks, such as climate change, cybersecurity threats, and pandemics. Insurers will collaborate with data scientists, climatologists, and other experts to assess and manage these evolving risks.
Global Ecosystems and Cross-Border Operations: With the advancement of technology, insurance ecosystems will be increasingly global. Insurers will collaborate across borders, offering coverage to customers in different countries and expanding their market reach.
SimpleSolve’s core platform - SimpleINSPIRE is a future-ready API-based architecture that integrates and leverages innovation from insurtech providers to enable a context-specific, data-driven approach to almost all business functions of the insurer. We are continuously forging partnerships with insurtech providers and have about 70+ insurtech interfaces that support our insurance partner’s digital transformation.
Topics: Digital Transformation








