Why Generative AI Is Getting Insurers Talking

Towards the end of 2022, the introduction of a user-friendly Generative AI chatbot sparked a wave of curiosity and innovation. It prompted a fresh perspective on the creative potential of this technology. Given the palpable enthusiasm and burgeoning interest in Generative AI, it becomes imperative to delve deeper into its potential capabilities and the far-reaching implications it holds for insurance.
In this article, we'll delve into what generative AI is, exploring how it works, its transformative impact on insurance from both developers' and insurers' perspectives, and the promising future that it could herald. For insurers ready to embark on this journey, there are a few practical insights on how to get started and seamlessly integrate generative AI into your existing technology landscape.
What Is Generative AI and How Does It Work?
Generative AI is the magic wand of artificial intelligence because it has the ability to create new content, be it text, images, or music. The surprising part is that what it generates cannot often be differentiated from human-produced content. But how does this apparent wizardry work?
At its core, Generative AI leverages machine learning techniques to create data models that mimic the input data it's trained on. The technology used is the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), consisting of two players: the generator and the discriminator.
The generator crafts new data, while the discriminator assesses its authenticity, trying to see if it can find a difference between the real and the AI-generated. The two are pitted against each other and as they learn from each other, both get better over time. Ultimately churning out high-quality data that is practically indistinguishable from the real deal.
Generative AI models are usually data-hungry and require intensive computational power. This is why Generative AI models and APIs are provided by various organizations and companies making it much easier for businesses to develop their own customized solutions by using pre-trained models. Some notable providers include OpenAI, Google (e.g., with models like BERT and T5), Microsoft (e.g., with models like GPT-3 and BERT), and Amazon (e.g., with services like Amazon SageMaker and Lex). These providers offer access to their models through cloud-based APIs, enabling developers to integrate and fine-tune them into their applications
Generative AI’s Impact: From the Perspective of Developers and Insurers
From the developer's standpoint, generative AI is a game-changer. It offers the opportunity to automate processes at a faster pace. This means developers don't have to write extensive code for user interactions; instead, they can focus on training the AI to understand and respond to user queries in plain language.
Developers are embracing generative AI models like GPT 3.5 and GPT 4 and the expanding universe of new successors to supercharge insurance operations, resulting in increased efficiency and effectiveness across the board. A note of caution must be brought in here, right now the existing models have the ability to generate code that works for smaller programs but not as yet to the extent of integrating complex solutions.
Now, let's shift our gaze to insurers. They are evaluating generative AI with three primary objectives on their radar:
-
Enhancing Customer Experiences: Insurers are looking to deploy generative AI virtual assistants, revolutionizing customer service and product creation. If you have recently interacted with a generative AI tool, it would have been hard to miss how exactly like an actual human its written responses are. SimpleInspire's Tara can provide context-based interaction with you and with the system. Tara can also trigger external Insurtech services and use or display the results within SimpleINSPIRE.
-
Boosting Productivity:. To enhance productivity and efficiency in the insurance industry, consider integrating generative AI alongside your team of experts, including underwriters, actuaries, claims adjusters, and engineers. Generative AI can summarize and synthesize vast volumes of data such as call transcripts or legal documents. This is where it can make the biggest impact on insurance processes including streamlined claims processing, accelerated decision-making, and improved customer interactions.
-
Managing Compliance and Mitigating Risks: In the heavily regulated insurance industry, compliance and risk mitigation are top priorities. Generative AI is stepping in to monitor compliance, detect fraud, and even generate training materials to keep staff up-to-date on the latest regulations.
The Future of Generative AI in Insurance
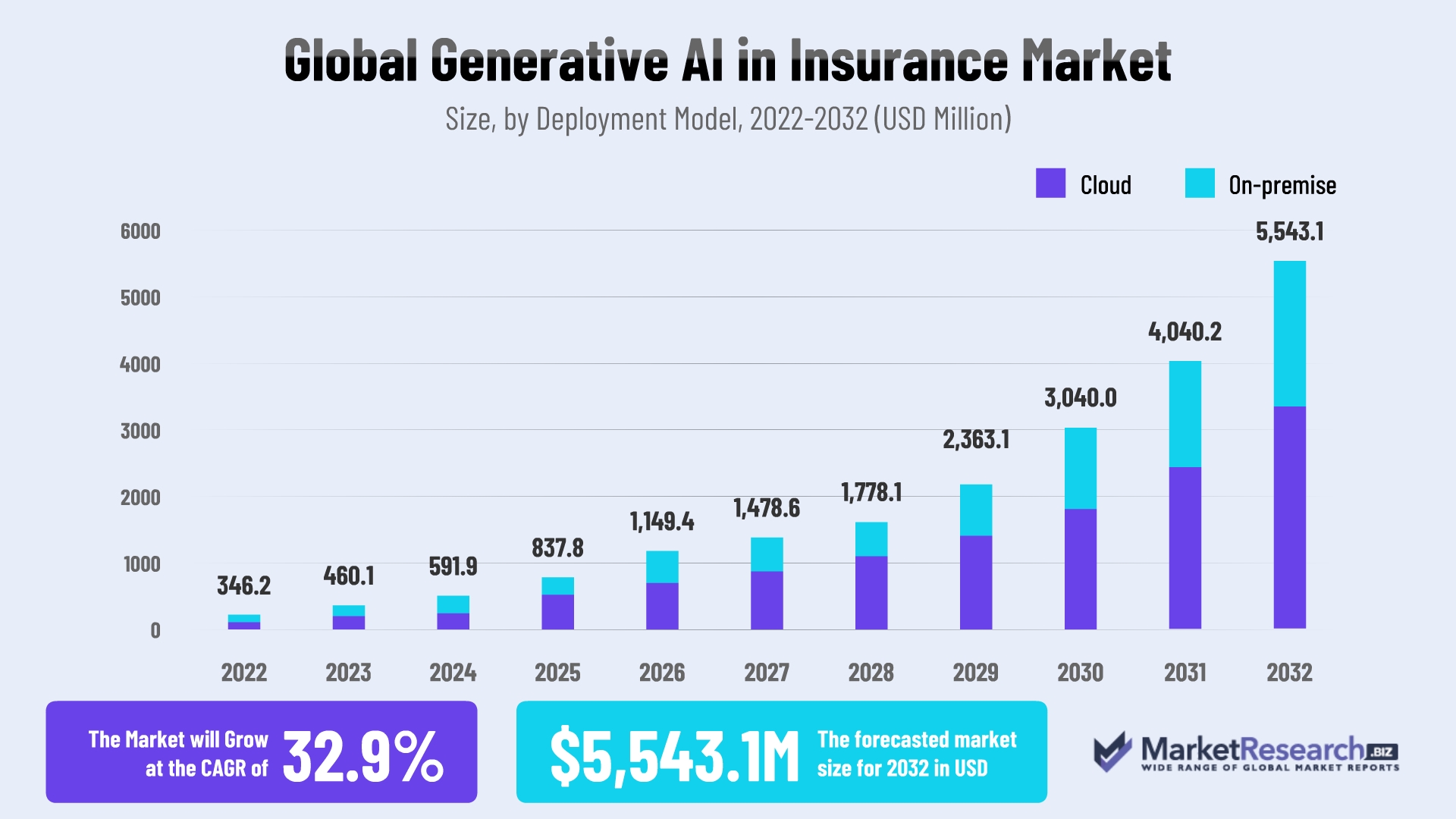 The road ahead for generative AI in insurance is promising. As more insurers explore this technology, generative AI use cases are set to multiply.
The road ahead for generative AI in insurance is promising. As more insurers explore this technology, generative AI use cases are set to multiply.
The generative AI insurance market is poised for significant growth. According to Enterprise Apps Today, it's projected to reach approximately USD 5543.1 million by 2032. This growth will be driven by insurance companies' increasing adoption of generative AI to streamline operations and elevate customer engagement.
The future integration of generative AI for insurance processes:
-
Summarize Policies and Documents: One of the most effective Generative AI use cases will be in summarizing complex policies, documents, and unstructured content with remarkable accuracy. In fact, recent data from leading insurers indicates that generative AI could reduce the time needed for policy summarization by up to 60%, enabling faster decision-making and improving customer service.
-
Synthesize Summarizations: Beyond mere summarization, generative AI will go a step further, synthesizing these summaries to create entirely new content. This innovation could rewrite the way insurers approach data and knowledge generation.
Thanks to its prowess in summarization and synthesis, generative AI can now answer intricate questions by drawing upon the vast knowledge it has acquired. It's like having an encyclopedia that evolves with every query.
-
Language and Code Translation: Generative AI in insurance will break down language barriers, effortlessly translating between natural languages eg. from English to Italian.
In the insurance industry, this multilingual capability will enable insurers to easily expand their global reach and offer policies in multiple languages, resulting in a potential 25% increase in international policy sales.
Also Read: Gen AI's Big Wins in Insurance But What About The Risks?
Getting Started with Generative AI: Adapting Existing Technology
For insurers looking to embark on this transformative journey, these initial steps are recommended:
-
Build a Multidisciplinary Team - Form a team comprising business experts, IT specialists, and data scientists. This team will focus on customizing generative AI solutions to suit the organization's unique needs.
-
Assess Current Infrastructure: The first step is to conduct a thorough assessment of the current technology infrastructure. This involves identifying the strengths and weaknesses of existing systems, understanding data storage and management processes, and evaluating the scalability of the platform. This may involve upgrading hardware, leveraging cloud-based solutions, or utilizing distributed computing.
-
Data Readiness: Generative AI relies heavily on data. Insurers should ensure that their data is clean, well-organized, and easily accessible. This may involve data cleansing, normalization, and the creation of data pipelines to ensure a smooth flow of information for AI models.
-
AI Governance Framework: Establish a robust AI governance framework that includes data privacy, security, and compliance protocols. This is critical, especially in the insurance sector, where sensitive customer information is handled.
-
Data Integration: Generative AI works best when it can access a wide range of data sources. Insurers should integrate data from various channels, including customer interactions, claims data, market trends, and regulatory updates.
-
Collaboration with AI Experts: It's essential to collaborate with AI experts or partner with AI development companies experienced in Generative AI. These experts can help insurers understand the specific use cases, develop AI models, and ensure seamless integration.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that Generative AI implementations align with industry regulations and compliance standards. Collaborate with legal experts to navigate the regulatory landscape and ensure data protection and ethical AI usage.
-
Develop Expertise Gradually - Start with low-barrier use cases and gradually fine-tune models based on domain knowledge and data sources. Combine multiple AI technologies to address different aspects of projects, optimizing processes for maximum benefits.
Drawing from our insights and expertise, we advise business leaders to exercise caution and avoid hasty leaps into the hype surrounding Generative AI. Seek support, knowledge, and collaboration from trusted partners and reputable third-party organizations with expertise in this domain. Leveraging the collective wisdom of those operating in this space can prove invaluable on your journey.
Topics: A.I. in Insurance






.jpg)